Sources of Law in Malaysia
FEDERAL LEGISLATION 4 types of Act. Unwritten laws are laws which are not contained in any statutes and can be found in case decisions.

Acca F4 Corporate Law Written Unwritten Law
Source of law in Malaysia.

. In United Malayan Banking CorpBhd. However not all of Englands common law and rules of equity form part of Malaysian law. Malacca-Section 52 of the Civil.
110 SOURCES OF LAW. Law and unwritten law. The 13 Constitution of the States comprising the Federation.
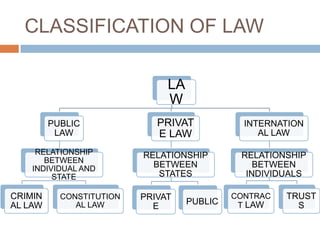
It is quite different with England their main source. Sources of law in Malaysia are consist of three main law which are Written Law Unwritten Law and Islamic Law. Written law is the most important source of law.
The sources of Malaysian law means the legal rules that make the laws in Malaysia which can be classified into written and unwritten law. Federal Court Rules 1995 PU. Terms in this set 7 Federal constitution-a written documents which lay down the power at the federal government.
Malaysia practices the mixed legal system which consists of the Customary Law Islamic Law and Common Law. Religious in common law and beliefs local customs opinion rules of equity. A 5241994 Rules of Court 2012 PU.
Written laws are laws which have been enacted in the constitution or in legislation. Federal law made by Parliament. It shapes politics economics and society in numerous ways and serves as a social mediator of relations between people.
In Malaysian Legal System the most important source of law is the Written Law which comprises of The Federal Constitution. Written law Unwritten law and Islamic law. Sources of Law in Malaysia The Federal Constitution in Article 1602 defines law to include three sourcesi written law ii the common law and iii any custom having the force of law.
The sources of Malaysian legal system law are from two different laws which are the Written and Unwritten law. Sources OF Malaysian Law unwritten law sources of law historical. English law forms part of the laws of Malaysia.
LAW Introduction The source of Malaysian law can be classified into 1. Subsidiary or Delegated Legislation -Subsidiary legislation is defined as any proclamation rule regulation order notification by-law or other instrument made under any Ordinance Enactment or other lawful authority and. Description of the Malaysian Courts.
The National Land Code is a complete and comprehensive code of law governing the tenure of land in malaysia and the incidents of it as well as other important matters affecting land there and there is no room for the importation. SOURCES OF MALAYSIAN LAW The legal rules of Malaysian law can be classified into written law unwritten law and MuslimIslamic law. English law can be found in the English common law and rules of equity.
Up to 3 cash back SOURCES OF MALAYSIAN. SOURCES OF MALAYSIAN LAW d. A 3761995 Court of Appeal Rules 1994 PU.
Of jurists of the. A Sources of law is the authority from which the law derives their forces. Written law is the law that has been enacted by the legislature or constitutions while unwritten law is the law that has not been enacted by any legislature or constitutions.
The Malaysian Legal System is based on English common law. Written law is the most important source of law among these three laws which includes the Federal Constitution legislation and subsidiary legislation. Law is a system of rules and guidelines which are enforced through social institutions to govern behaviour wherever possible.
This means that legislation subsidiary legislation judicial precedents and recognized customs are the source of law in Malaysia. This is known as the common law or case. Essay Sample Check Writing Quality.
The main sources of law in Malaysia can be categories as follows. Sources of Law in Malaysia. Act main Act like Contract Act 1950 Amendment Act changes in Principal Act Revised Act changes made by Commisioner of Law Reform such as Civil Law Act 1956 Revised 1972 Consolidated Act bring together simple Act or more on specific matters.
The most important law among the three laws is the Written Law. Into Peninsular Malaysia except Penang and. 33 Case Law as a principal source of law.
First of all I would like to brief to you about the sources of law in Malaysia. The sources of law in Malaysia can be divided into two types which are written laws and unwritten laws. The Malaysia Act 1963 created the State called Malaysia which is made up of eleven states of the former Federation of Malaya Sabah Sarawak and Singapore.
Contract law regulates everything from buying a bus ticket to trading on. The sources of Malaysian law The laws of Malaysia can be divided into two types of laws written law and unwritten law. Written law is the law that has been enacted by the.
The sources of law in Malaysia can be divided into two types which are written laws and unwritten laws. History of its Development. Overview of Malaysias Judicial System.
The laws of Malaysia can be divided into two types of lawswritten. It refers to the laws contained in the Federal and State Constitutions and in a code or a statute. V Pemungut Hasil Tanah Kota Tinggi 1984 2 MLJ 87 the Privy Council noted.
In 1965 Singapore left Malaysia and became an independent State. Law Act 1956 applied to. Section 3 1 of the Civil Law Act 1956 Revised 1972 provides that in Peninsular Malaysia the courts shall apply.
It also can define as legal rules that make up the laws in Malaysia. The Federal Constitution is a kind of higher law of the land which is used to. Written laws are laws which have been enacted in the constitution.


No comments for "Sources of Law in Malaysia"
Post a Comment